Finding and Vetting Kitchen Cabinet Staining Contractors

Transforming your kitchen with a fresh coat of stain on your cabinets is a rewarding project, but choosing the right contractor is crucial for a successful outcome. Careful vetting ensures a smooth process, a beautiful result, and protects your investment. This section Artikels the key steps to take when selecting a professional for your cabinet staining needs.
Contractor Qualification Checklist
Before contacting any contractor, prepare a list of questions to assess their suitability. This proactive approach helps you avoid potential problems and ensures you’re working with a reliable and experienced professional. Key areas to investigate include licensing, insurance, and demonstrable experience in kitchen cabinet staining. Asking these questions will give you a clearer picture of their capabilities and professionalism.
- Verify contractor’s state licensing and ensure it’s current and valid.
- Confirm they carry general liability and workers’ compensation insurance, protecting you from potential financial liabilities.
- Request a portfolio showcasing previous kitchen cabinet staining projects, paying close attention to the quality of their work and attention to detail.
- Inquire about their experience with different types of wood and stain finishes, ensuring they’re familiar with your specific cabinet material.
- Ask about their preparation methods, including sanding, cleaning, and priming techniques, to understand their approach to achieving a high-quality finish.
- Seek references from previous clients to gain firsthand insights into their work ethic, communication, and overall client satisfaction.
Obtaining and Comparing Contractor Quotes
To ensure you’re getting a fair price and understanding the scope of work, it’s vital to obtain at least three quotes from different contractors. This comparative analysis will help you make an informed decision based on pricing, timelines, and proposed methods. Remember that the lowest price isn’t always the best option; consider the overall value and quality offered.
| Contractor Name | Price | Timeline | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Staining Solutions | $3500 | 2 weeks | Spray staining with two coats of polyurethane |
| XYZ Cabinet Refinishing | $4000 | 3 weeks | Brush staining with three coats of lacquer |
| 123 Cabinet Masters | $3800 | 2.5 weeks | Spray staining with one coat of polyurethane and hand-rubbed finish |
Sample Kitchen Cabinet Staining Contract
A well-defined contract protects both you and the contractor. It should clearly Artikel the project’s scope, payment schedule, warranty information, and dispute resolution procedures. A sample contract would include details such as specific stain type, number of coats, preparation methods, and cleanup procedures. A clear contract minimizes misunderstandings and ensures a professional and transparent process.
This contract Artikels the agreement between [Client Name] and [Contractor Name] for the staining of kitchen cabinets. The total cost is [Price], payable as follows: [Payment Schedule]. The project will be completed within [Timeline]. A [Warranty Period] warranty covers defects in workmanship. Disputes will be resolved through [Dispute Resolution Method].
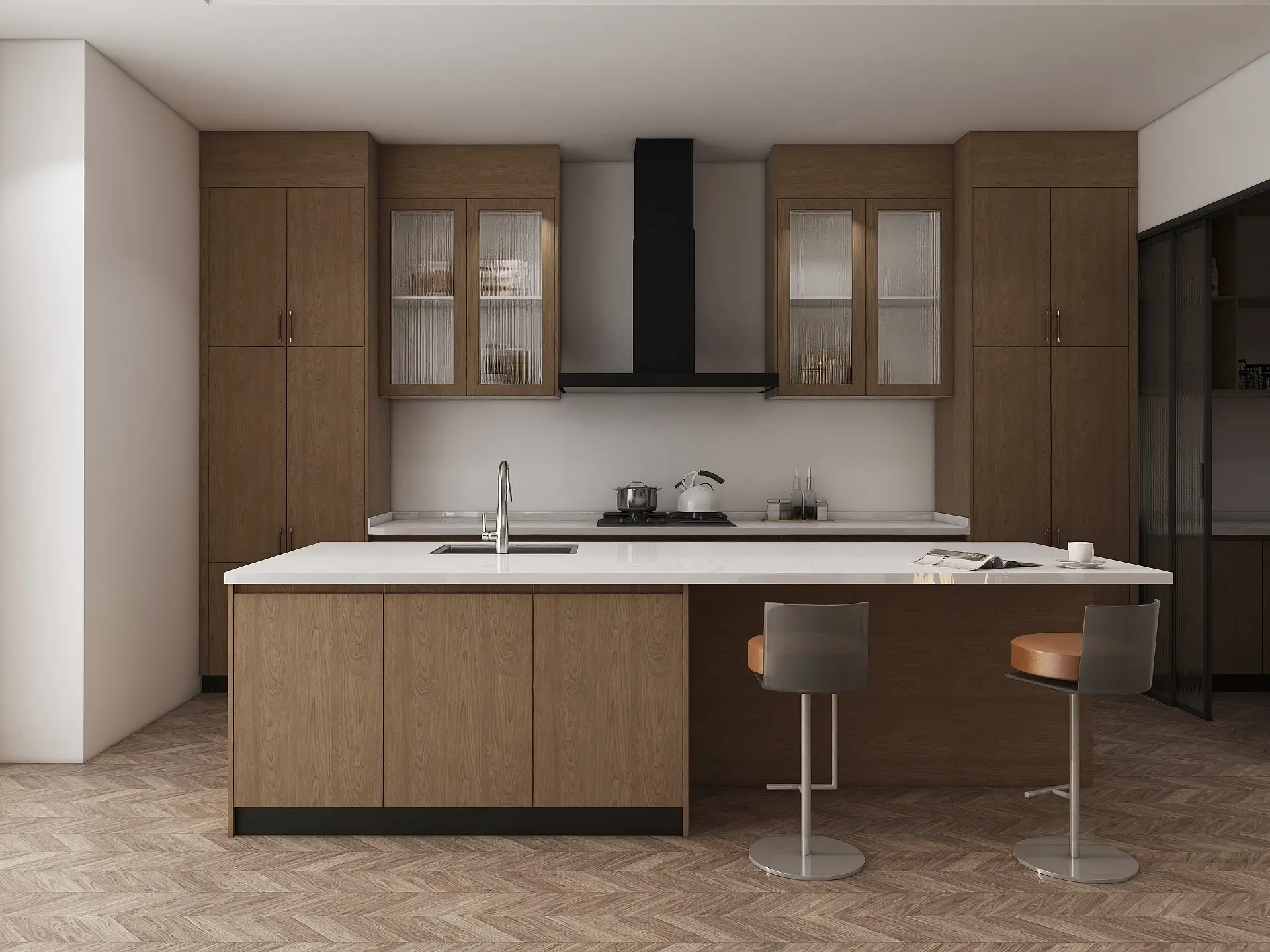
The Kitchen Cabinet Staining Process
Transforming your kitchen with a fresh coat of stain can dramatically enhance its aesthetic appeal and value. The process, while seemingly straightforward, requires careful planning and execution to achieve a professional-looking finish that will last for years. Understanding the different stain types and the step-by-step procedure is key to success.
Stain Types and Their Properties, Kitchen cabinet staining contractors
Choosing the right stain is crucial for achieving the desired look and durability. Different stain types offer unique advantages and disadvantages, impacting both the application process and the final result. Consider these factors when making your selection.
- Oil-Based Stains: Oil-based stains penetrate deeply into the wood, resulting in rich, vibrant color.
- Advantages: Deep penetration, rich color, longer open time for blending, forgiving of mistakes.
- Disadvantages: Strong odor, longer drying time, requires mineral spirits for cleanup, may yellow over time.
- Water-Based Stains: Water-based stains are a more environmentally friendly option, with lower VOCs (volatile organic compounds).
- Advantages: Low odor, fast drying time, easy cleanup with soap and water, less likely to raise the grain.
- Disadvantages: Can be less vibrant than oil-based stains, may require multiple coats for deep color, less forgiving of mistakes.
- Gel Stains: Gel stains are thicker than oil or water-based stains, making them ideal for vertical surfaces and filling imperfections.
- Advantages: Excellent for vertical surfaces, hides imperfections, less likely to run or drip.
- Disadvantages: Can be more difficult to blend, slower drying time, may require more coats for even color.
Step-by-Step Staining Process
The staining process involves several crucial steps, each contributing to the final quality and longevity of the finish. Careful attention to detail at each stage is essential.
- Surface Preparation: This is the most critical step. Begin by thoroughly cleaning the cabinets to remove grease, dirt, and grime. Then, sand the surfaces with progressively finer grit sandpaper (e.g., 120, 180, 220 grit) to create a smooth, even surface for stain penetration. Remove all sanding dust with a tack cloth. For heavily damaged cabinets, consider using wood filler to repair any significant imperfections before sanding.
- Priming (Optional): Priming is especially helpful with porous woods or when covering significant color differences. A good quality wood primer will create a uniform surface for stain application, preventing uneven absorption.
- Stain Application: Apply the stain using a brush, rag, or sprayer, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Work in the direction of the wood grain for a more natural look. Allow the stain to penetrate for the recommended time before wiping away any excess with a clean rag. Multiple thin coats are generally preferable to one thick coat.
- Topcoat Application: Once the stain is completely dry, apply a protective topcoat. This protects the stain from scratches, wear, and moisture damage. Polyurethane is a popular choice, offering durability and a clear, glossy finish. Apply multiple thin coats, sanding lightly between coats with fine-grit sandpaper to ensure a smooth surface.
Maintaining Stained Kitchen Cabinets
Proper maintenance is crucial for preserving the beauty and longevity of your stained cabinets. Regular cleaning and occasional polishing will keep them looking their best.
- Cleaning: Regularly wipe down cabinets with a damp cloth and mild detergent. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners that can damage the finish. For stubborn stains, use a specialized wood cleaner.
- Polishing: Periodically apply a wood polish or conditioner to help maintain the luster and protect the wood. This helps replenish oils and prevents drying.
- Addressing Minor Damage: Minor scratches can often be buffed out with a fine-grit sandpaper and wood polish. For more significant damage, consult a professional for repair or refinishing.
Cost and Considerations for Kitchen Cabinet Staining

Staining your kitchen cabinets can dramatically transform your space, but understanding the associated costs is crucial for budgeting and planning. This section breaks down the typical expenses, compares staining to other cabinet renovation options, and highlights factors influencing the final price. Remember, these are estimates, and your actual costs may vary depending on your specific project.
Typical Costs Associated with Kitchen Cabinet Staining
The cost of staining kitchen cabinets involves several key components. A detailed breakdown helps homeowners prepare a realistic budget. The following table provides a general overview of these expenses.
| Cost Category | Low-End Estimate | Mid-Range Estimate | High-End Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials (stain, sealant, sandpaper, etc.) | $200 – $500 | $500 – $1000 | $1000 – $2000 |
| Labor (professional staining) | $1000 – $2000 | $2000 – $4000 | $4000 – $8000 |
| Cabinet Repairs (if needed) | $0 – $500 | $500 – $1500 | $1500 – $3000 |
| Hardware Replacement (optional) | $0 – $300 | $300 – $800 | $800 – $2000 |
| Total Estimated Cost | $1200 – $3000 | $3300 – $7300 | $7300 – $15000 |
Note: These estimates are based on a medium-sized kitchen. Larger kitchens will naturally increase costs. DIY projects can significantly reduce labor costs, but may require additional time and expertise.
Cost-Effectiveness of Staining vs. Repainting or Refacing
Choosing between staining, repainting, or refacing cabinets depends on your budget, desired aesthetic, and the condition of your existing cabinets. Staining generally offers a more natural look and can enhance the wood grain, while repainting provides a more uniform finish. Refacing involves replacing cabinet doors and drawer fronts, offering a significant visual upgrade but at a higher cost.
For example, staining solid wood cabinets in good condition might cost significantly less than refacing them, which can be two to three times more expensive. However, repainting severely damaged cabinets might be more cost-effective than attempting to stain them, as extensive repairs would be needed beforehand. The choice depends on the specifics of your kitchen and your budget.
Factors Influencing Overall Cost
Several factors significantly impact the final cost of staining kitchen cabinets. The type of wood, the size of the kitchen, and the level of detail required all play a role.
Cabinet material: Solid wood cabinets are more expensive to stain than particleboard or MDF cabinets because they require more careful preparation and staining techniques. For instance, staining oak cabinets might require more time and labor due to the wood’s grain and density compared to staining simpler materials like MDF.
Kitchen size: The number of cabinets directly affects the amount of materials and labor needed. A larger kitchen with more cabinets will obviously cost more to stain than a smaller one.
Level of detail: Intricate detailing, such as raised panels or carvings, requires more precise work and increases the overall cost. Simple, flat-panel cabinets are generally less expensive to stain.
